











15 CV Cable Manufacturers in 2024
This section provides an overview for cv cables as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 15 cv cable manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked cv cable companies as of April, 2024: 1.LEONI Kabel GmbH, 2.B&H Foto and Electronics Corp., 3.Anixter Inc..
Table of Contents
What Is a CV Cable?
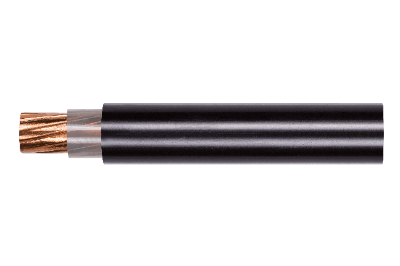 A CV cable, officially known as a "cross-linked polyethylene insulated vinyl sheath cable," is commonly used in industrial power transmission. It employs cross-linked polyethylene for insulation and vinyl for the sheath layer.
A CV cable, officially known as a "cross-linked polyethylene insulated vinyl sheath cable," is commonly used in industrial power transmission. It employs cross-linked polyethylene for insulation and vinyl for the sheath layer.
Uses of CV Cables
Primarily, CV cables facilitate power transmission. In urban areas, these cables are often seen suspended from utility poles as supports. Distinguished by their core wire covered with vinyl sheath or polyethylene, CV cables are designed to withstand outdoor elements like wind, rain, and sunlight. Unlike vinyl-sheathed cables used in household power distribution, CV cables are not typically found inside homes.
Principle of CV Cables
High-voltage CV cables typically consist of multiple layers: a core wire (usually copper or aluminum), a semiconducting layer, cross-linked polyethylene insulation, a copper tape layer, and a vinyl sheath. The core wire acts as the electrical pathway, often composed of twisted thin copper wires for flexibility.
The semi-conductive layer, made from carbon-rich polymers, surrounds the core wire, preventing voltage-related deterioration of the cross-linked polyethylene insulation. An additional semi-conductive layer is placed outside the insulation, leading up to the copper tape layer. This layer, a thin copper film, contains electromagnetic emissions from the core wire and acts as a grounding pathway in case of insulation failure. The outermost vinyl sheath, usually black, offers corrosion protection and improved weather resistance.
In multi-core cables, insulating fibers like jute are used as inclusions between the sheath and copper tape layer to fill gaps. These cables, often three-core for compatibility with 3-phase power transmission systems, may utilize a triplex construction for enhanced heat dissipation and are also referred to as CVT cables.
Other Information on CV Cables
Differences in CV Cables According to Voltage
The structure of CV cables varies depending on the voltage requirements:
1. CV Cables for Special High Voltage:
At special high voltage levels, the cross-linked polyethylene insulation is made thicker, and the copper tape layer is designed more like a flexible tube or wire rather than a tape, enhancing insulation and grounding capabilities.
2. 3.3KV CV Cables:
For 3.3kV applications, a semiconducting layer is replaced by an insulating material like PET. These cables use a single copper tape layer for grounding and have simpler end treatments compared to 6.6kV cables.
3. Low-Voltage CV Cables:
Low-voltage cables often omit the semi-conductive and copper tape layers due to lower electromagnetic emissions. The cross-linked polyethylene insulation is also thinner than that in high-voltage cables.
List of 15 CV Cable Manufacturers
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
- Default
- Company Size: largest first
- Year Founded: oldest first
- Year Founded: earliest first
Sort by Area
- United States of America
- China
- Germany
- Poland
- Taiwan
- Thailand
- United Kingdom
-
-

-
Anixter Inc.
MAGNET CRANE CABLE CV
Company Overview
Anixter Inc. is a distributor of electrical, electronic, and networking products. It is headquartered in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA and was established in 1922. The company distributes a wide range of products, including cables, connectors, switches, and sensors. Its products are used in many industries, including construction, manufacturing, and healthcare. The company also offers technical support, installation, supply chain and e-commerce, finance and, credit and training services to ensure efficient utilization of its products.
-
-
-
-

Distributor Overview
Sweetwater, established in 1979, is a dealer and supplier of high-technology equipment for musicians, recording studios, and broadcasters, based in the United States. The company, based in Fort Wayne, Indiana, offers a wide range of products from microphones and digital recording systems to electric guitars and electronic keyboards. It has grown significantly over the years, serving millions of customers and employing a team of thousands. Its constant emphasize on delivering uncommon service and unparalleled expertise has helped it become the #1 online retailer of pro audio and music instruments in the United States.
-
-
-
-

-
LEONI Kabel GmbH
cables ≥ 125 °C
Manufacturer Overview
LEONI Kabel GmbH, established in 1917 and based in Roth, Germany, is a manufacturer specializing in both standard and special automotive cables. The company's diverse product range includes cables featuring various conductor materials, high-voltage cables, as well as data and coaxial cables. These special cables play a vital role in data transmission, alternative drive systems, and power transmission within the automotive industry. LEONI Kabel GmbH also offers customer services that include the development of customized solutions, consultation, and warranty support.
-
-
-
-

-
Round Teck International Company
FR-CV
Manufacturer Overview
Round Teck International Company is a Taiwanese manufacturer of various connectivity products established in 1978 and based in New Taipei City, Taipei. The company’s product list includes various optical fiber cables, standard or silver plated copper wire, data and coaxial cables, ground braided wires, and power cables. It also produces cable accessories such as insulators, and braided expandable sleeving for added protection or durability. The company’s products are used by OEMs and ODMs in the consumer electronics and IT sectors, as well as by clients in the telecom and power distribution industries.
-
-
-
-

-
Phelps Dodge International Limited.
PHELPS DODGE CABLE TYPE CV

Manufacturer Overview
Phelps Dodge International (Thailand) Limited (PDITL), established in 1968 and based in Bangkok, Thailand, is a wire and cable manufacturer with 50 years in the industry. Its products include building, medium-voltage, telephone, and high-voltage wires. The company has a high-voltage testing unit that provides mobile testing services for high-voltage cables according to IEC standards. It uses VCV (vertical continuous vulcanization) to ensure quality and safety by making the conductors of high-voltage lines centered symmetrically. It has ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and OHSAS 18001 certifications and exports to more than 30 countries.
-
-
-
-

-
Keith McMillen Instruments
QuNexus CV Cable Kit
Manufacturer Overview
Keith McMillen Instruments is an American developer and manufacturer of musical computer interface technology products established in 2005 and based in Berkeley, California. The company produces MIDI keyboard and drum pad controllers, programmable digital mixer control surfaces, foot controllers, and bass pedal keyboard controllers that enable users to play or control music via computer GUIs. It also offers adapters, expanders, cymbal stand mounts, and patch cables. The company's products are mainly used by its clients in the music industry and educational institutions, as well as by hobbyist musicians.
-
-
-
-

-
Red Panda
CV to Expression Cable
Manufacturer Overview
Red Panda is an American manufacturer of effects pedals for electric or bass guitars and synthesizers established in 2009 and based in Detroit, Michigan. The company’s products include various pedals for altering the sound of instruments by adding effects such as distortion, delay, reverb, modulation, or granular shifting. Other products include brand logo totes and hoodies, software applications for updating pedal effects via USB, and accessories such as cable, adapters, and knobs. The company primarily serves clients in the music industry and educational institutions, and commonly retails to hobbyists and enthusiasts.
-
-
-
-

-
Jenuincable
XLPE Insulated Cable
Company Overview
Jenuincable, founded in 1999 and based in China, is a manufacturer and supplier of wires, cables and related accessories. Its products include control cables, electric wires, building wires, control cables, power cables, screen cables, flexible cables, LSZH cables, armoured cables and more. The company also manufactures customised cables according to the client's needs. The wires are supplied according to the standards of IEC, AS/NZS and BS. The company has all the necessary cable facilities to manufacture the cables in-house.
-
-
-
-

Company Overview
TME, established in 1989 and headquartered in Łódź, Poland, is a distributor specializing in electronic and electromechanical components, measurement and instrumentation equipment, tools, accessories, and development kits. Its product range encompasses resistors, capacitors, switches, multimeters, tools, and microcontroller development kits. TME serves diverse clientele, including electronics manufacturers, hobbyists, and educational institutions. The company offers support to an array of businesses and organizations in procuring essential components and equipment for electronic projects and manufacturing needs.
-
-
-
-

-
Revelation Cable Co.
Control Voltage (CV) Cable
Company Overview
Revelation Cable Co. is a Canadian custom cable manufacturer and supplier that was established in 2017 in Langley, British Columbia. The company produces various speaker, patch, and instrument cables, as well as MIDI protocol cables and pro audio data cables for transmitting audio data between devices. It also offers handmade power cables, as well as power and data cable adaptors. The company’s products are used primarily by client recording studios, music retailers, audio equipment manufacturers, and musicians.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-

-
Jeddah Cables Company
HIGH AND EXTRA HIGH VOLTAGE
-
-
-
-

-
B&H Foto and Electronics Corp.
Keith McMillen Instruments CV Cable Kit
Distributor Overview
B&H Foto & Electronics Corporation, founded in 1973 and based in Manhattan, New York City, is a retailer of photo, video, and other technological equipment. B&H is an authorized seller of Sony, Panasonic, Canon, Fuji, and more. The company serves photographers, musicians, and professionals with products related to film, music, photography, audio, art, and technology. The company's main products include photography gear, computers, televisions, drones, surveillance systems, and more. B&H store has nearly 500,000 items in stock for customers who need them.
-
-
CV Cable Manufacturer Ranking
*Including some distributors, etc.Ranking as of April 2024
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | LEONI Kabel GmbH |
15.2%
|
| 2 | B&H Foto and Electronics Corp. |
13.0%
|
| 3 | Anixter Inc. |
13.0%
|
| 4 | Sweetwater |
8.7%
|
| 5 | Jenuincable |
8.7%
|
| 6 | TME |
8.7%
|
| 7 | BANGKOK CABLE CO., LTD. |
6.5%
|
| 8 | Phelps Dodge International Limited. |
6.5%
|
| 9 | Caledonian Cables Ltd |
4.3%
|
| 10 | Revelation Cable Co. |
4.3%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the cv cable page as of April 2024. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
- Kable-X Technology Suzhou Co., Ltd.: 2015 (9 years ago)
- TME: 1989 (35 years ago)
- Jeddah Cables Company: 1989 (35 years ago)
Company with a History
- Anixter Inc.: 1957 (67 years ago)
- BANGKOK CABLE CO., LTD.: 1964 (60 years ago)
- Phelps Dodge International Limited.: 1968 (56 years ago)
CV Cable Manufacturers in United States
*Including some distributors, etc.
Global Distribution of CV Cable Manufacturers by Country
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
2 | 20.0% |
 Thailand
Thailand
|
2 | 20.0% |
 China
China
|
2 | 20.0% |
 Germany
Germany
|
1 | 10.0% |
 Taiwan
Taiwan
|
1 | 10.0% |
 Poland
Poland
|
1 | 10.0% |
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
|
1 | 10.0% |
